Spring Boot + RabbitMQ Architecture
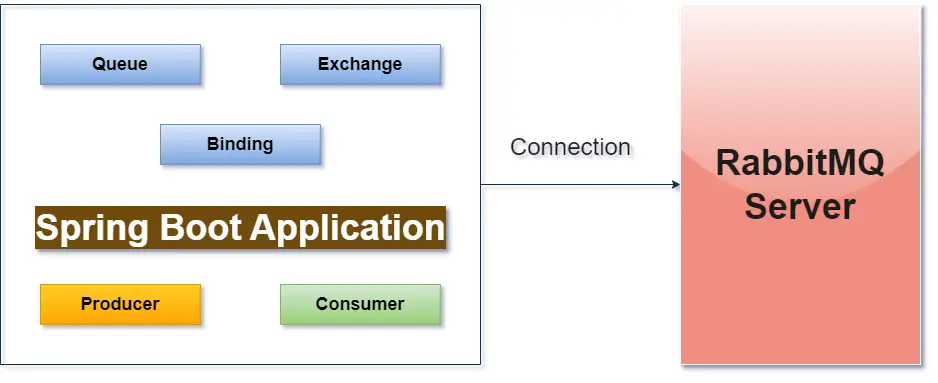
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have the following tools and dependencies installed:
- Java JDK (8 or higher)
- Spring Boot
- RabbitMQ Server (installed and running)(For RabbitMQ configuration please see RabbitMQ Configuration on ubuntu or windows.)
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Setup Spring Boot Application
If you do not have spring boot application then got to spring initializr and build the project. While building the project then add given dependency.
- Spring for RabbitMQ
- Spring AMQP(RabbitMQ)
- Spring Web
- Lombok
Step 2: Spring Boot Auto Configuration for spring AMQP(RabbitMQ).
Go to application.properties file and configuration given properties for RabbitMQ connection.
##RabbitMQ Connection Configuration
spring.application.name=rabbitmqDemo
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
## rabbitmq
rabbitmq.queue.name=stringQueue
rabbitmq.exchange.name=exchange
rabbitmq.routing.key=stringRouting
## rabbitmq json
rabbitmq.queue.json.name=jsonQueue
rabbitmq.routing.json.key=jsonRouting
Step 3: Create given packages under application.
- config
- consumer
- controller
- dto
- publisher
Step 4: Configure Queue and Exchange.
Go to config package and create RabbitMQConfig class.
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class Config {
@Value("${rabbitmq.queue.name}")
private String queue;
@Value("${rabbitmq.queue.json.name}")
private String jsonQueue;
@Value("${rabbitmq.exchange.name}")
private String exchange;
@Value("${rabbitmq.routing.key}")
private String routingKey;
@Value("${rabbitmq.routing.json.key}")
private String jsonRoutingKey;
// spring bean for string queue
@Bean
public Queue queue() {
return new Queue(queue);
}
// spring bean for string exchange
@Bean
public TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange(exchange);
}
// spring bean for binding between queue and exchange with routing key
@Bean
public Binding binding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue())
.to(exchange())
.with(routingKey);
}
// For string no need to create given beans
// A) Rabbit Template
// B) Connection Factory
// C) Rabbit Admin
// spring bean for json queue
@Bean
public Queue jsonQueue() {
return new Queue(jsonQueue);
}
// spring bean for binding between queue and exchange with routing key for json
@Bean
public Binding jsonBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(jsonQueue())
.to(exchange())
.with(jsonRoutingKey);
}
// message convertor
@Bean
public MessageConverter convertor() {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
// create rabbitmq template for json
@Bean
public AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
rabbitTemplate.setMessageConverter(convertor());
return rabbitTemplate;
}
}
In this configuration class:
- queue() and exchange() bean return queue name and exchange name respectively for string message.(producer send string message to RabbitMQ)
- binding() bean for binding between queue and exchange with routing key for string message.(producer send string message to RabbitMQ)
- For string message no need to create Rabbit Template and Connection Factory
- jsonQueue() bean return jsonQueue name.(producer send JSON message to RabbitMQ)
- jsonBinding() bean for binding between jsonQueue and exchange with jsonRouting key for JSON message.(producer send JSON message to RabbitMQ)
- convertor() bean use for message convertor.
- amqpTemplate() bean use for JsonTemplate.(producer send json message to RabbitMQ)
Step 5: Create RabbitMQ Procedure
Go to publisher package and
- Create RabbitMQProducer class for send message(string message) to RabbitMQ Queue.
- Create RabbitMQJsonProducer class for send json message to RabbitMQ Queue.
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class RabbitMQProducer {
@Value("${rabbitmq.exchange.name}")
private String exchange;
@Value("${rabbitmq.routing.key}")
private String routingKey;
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQProducer.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String message) {
LOGGER.info("Message send:: [{}]", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message);
}
}
Send JSON Message to RabbitMQ Server
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.fullstackblogs.rabbitmqDemo.dto.User;
@Service
public class RabbitMQJsonProducer {
@Value("${rabbitmq.exchange.name}")
private String exchange;
@Value("${rabbitmq.routing.json.key}")
private String jsonRoutingKey;
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQJsonProducer.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage(User user) {
LOGGER.info("Message json send:: [{}]", user);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, jsonRoutingKey, user);
}
}
Step 6: Create Rest API to Send Message
Go to controller package and
- Create MessageController class for send string message
- Create MessageJsoncController class for send json message
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.fullstackblogs.rabbitmqDemo.publisher.RabbitMQProducer;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/v1")
public class MessageController {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQProducer.class);
@Autowired
private RabbitMQProducer rabbitMQProducer;
@GetMapping(value = "/publish")
public ResponseEntity sendMessage(@RequestParam("message") String message){
rabbitMQProducer.sendMessage(message);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Message send to the queue ...");
}
}
MessageJsonController Class
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.fullstackblogs.rabbitmqDemo.dto.User;
import com.fullstackblogs.rabbitmqDemo.publisher.RabbitMQJsonProducer;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/v2/")
public class MessageJsoncontroller {
@Autowired
private RabbitMQJsonProducer rabbitMQJsonProducer;
@PostMapping(value = "publish")
public ResponseEntity sendJsonMessage(@RequestBody User user){
rabbitMQJsonProducer.sendMessage(user);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Message send to exchange ...");
}
}
Step 7: Create Rest API to Send Message
Go to consumer package and
- Create RabbitMQConsumer Class for receive string message
- Create RabbitMQJsonConsumer Class for receive JSON message
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Backoff;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Retryable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQConsumer.class);
@RabbitListener(queues = "${rabbitmq.queue.name}", concurrency = "5")
@Retryable(value = { Exception.class }, maxAttempts = 3, backoff = @Backoff(delay = 1000))
public void consumer(String message) {
LOGGER.info("Message Recieved :: [{}]", message);
}
}
JSON Message Consumer Class
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.fullstackblogs.rabbitmqDemo.dto.User;
@Service
public class RabbitMQJsonConsumer {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQJsonConsumer.class);
@RabbitListener(queues = "${rabbitmq.queue.json.name}")
public void consumeJsonMessage(User user) {
LOGGER.info("Message Recieved :: [{}]",user);
}
}
Step 8: Go to dto package and create user POJO class
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
}
Now you can run your application and hit given url form postman
For publish string message
- http://localhost:8080/api/v1/publish?message=Hello RabbitMQ
- Api Type:- GET
For publish JSON message
- http://localhost:8080/api/v2/publish
- API TYPE:- POST
- Body:- {“id”: 1, “firstName”: “XYZ”,”lastName”: “XXXX”}
Download complete code here
That’s All

